It’s not a secret that the modern Internet is being influenced by such giants of the tech world as Facebook, Google, Microsoft and Amazon. Today, the majority of global Internet traffic is already being transferred through private networks, and CDN (content delivery networks) also comprise those. According to Cisco’s annual forecast of Internet traffic trends, in a few years, this proportion is said to increase to over 70%.
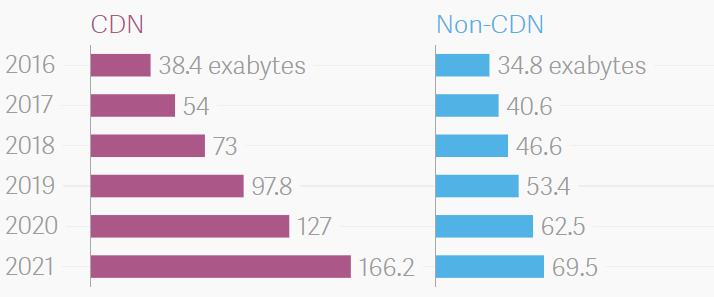
CDN networks serve to boost user experience by accelerating transfer of online media, especially video streams and broadcasting. Although this technology is not new, it may have a great impact on the Internet simply due to the amount of traffic it’s used to handle. Such networks are often preferred by third-party telecommunication companies that deal with enterprises, for instance, Akamai and Limelight. Rising popularity of video streaming triggered massive investment from consumer-facing companies like Google, Facebook and Netflix. This growing proportion of traffic over CDNs has resulted into such phenomenon as “flattening” of the Net.
CDNs are expected to dominate in some particular areas, especially wealthy ones. These include Western Europe, North America, and Asia Pacific. The same mentioned report made by Cisco states that about 91% of Internet traffic in America will be transferred via CDN by 2021, while it’ll be only 31% in Africa and the Middle East.
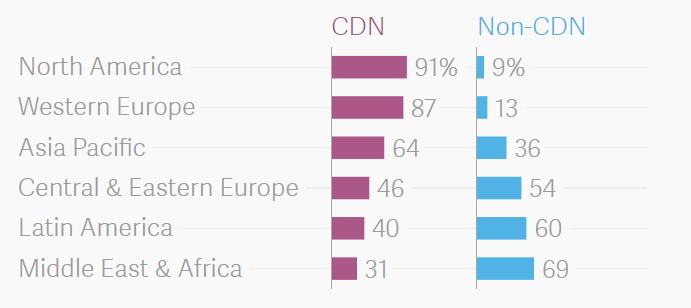
Internet traffic flow over CDNs in 2021
Top dogs like Facebook, Amazon, Netflix, and Google keep increasing investment into their own CDNs to serve content for their users. Cisco also predicts that the proportion of traffic via these giant networks will also be more tremendous in wealthier regions. About 60% of traffic will be served via private CDNs. A case in point is a CDN set up by Netflix in North America by 2021. This year, only 10% of traffic in Africa and Middle East are transferred over a private CDN.
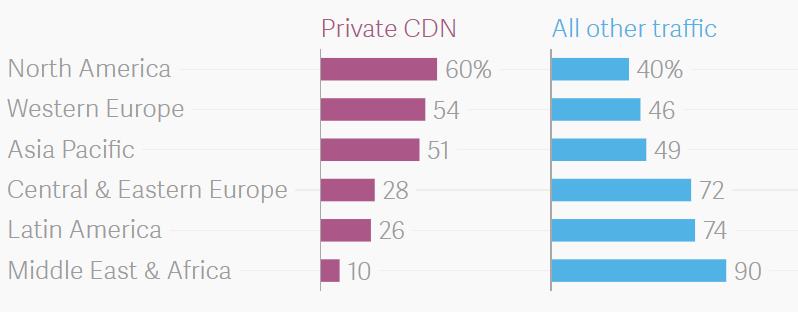
Internet traffic flow over private CDNs by 2021
What can’t be denied is that users served by CDNs have much better experience: they enjoy lag-free gaming, smooth and high-quality video streaming, movies without buffering, and so on. Every mile that video content has to travel degrades the quality of files and hurts user experience.
Does it mean that the lag of CDN services in some certain areas makes up for a new digital divide? Not likely. Just like any other Internet service, CDN will gradually become cheaper and more affordable for less wealthy countries, and with a growing demand for it, we will see further investment.




in social networks